Flame Retardants
Do they save lives or cause harm?
What are flame retardants?
Flame retardant chemicals are added to products including furniture foam, electronics, children’s products, and building insulation to meet flammability standards. Unfortunately, these standards are often poor predictors of real-life fire risks and lead to the unnecessary use of these toxic chemicals.
Some flame retardants are associated with elevated cancer risk, developmental and reproductive harm, and hormone disruption. Learn what you can do.
Learn more about products that may contain flame retardants.
How are we exposed?
Flame retardants are usually additive rather than reactive. This means they are physically mixed with the materials in products rather than chemically bound. Flame retardants can continually migrate out of products and into dust, food, and water, all of which we ingest. We can also be exposed by breathing in the vapors of these chemicals, or through skin contact, particularly when flame retardant chemicals stick to our cell phones or clothing.
Flame retardants are detected in the bodies of nearly all people tested. Due to their frequent hand-to-mouth behavior, young children have the highest levels of exposure. Their developing bodies are also particularly vulnerable to these chemicals’ harmful effects.
What are the concerns?
Flame retardants are often:
PERSISTENT: Do not break down in the environment. We can continue to be exposed from food and products years after a chemical is banned or phased out.
BIOACCUMULATIVE: Build up in people and other animals, especially at the top of the food chain.
MOBILE: Travel long distances and have been found at the Earth’s poles and the ocean’s depths.
TOXIC: Associated with increased cancer risk, impaired neurological and reproductive development.
Should flame retardants be used?
Flame retardants often delay ignition only a few seconds and can make fires more dangerous due to increased smoke and toxic gases. When organohalogen flame retardants are present, fires produce halogenated dioxins and furans, which may contribute to elevated rates of cancer in firefighters.
Self-extinguishing cigarettes, photoelectric smoke detectors, sprinkler systems, fire safety education, and accessible escape routes are more effective and healthier ways to prevent fire deaths.
In cases when flame retardants are necessary, manufacturers should develop safer alternatives using design and material innovation and green chemistry.
Flame retardants of concern
Flame retardants that harm health are often organic chemicals, meaning they contain carbon atoms. They may be organohalogens (contain chlorine or bromine bound to carbon), organophosphates (contain phosphorus surrounded by oxygen atoms bound to carbon), or both.
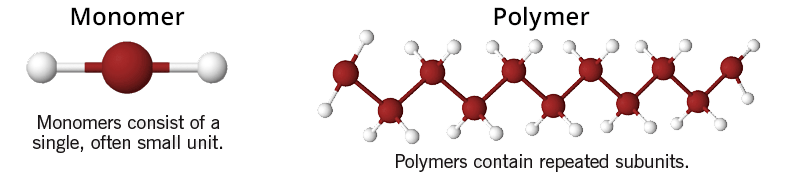
Flame retardants are monomeric or polymeric. Monomers consist of a single, often small unit: like a lego block. Polymers contain repeated subunits which may include toxic halogens and phosphates: like a chain of legos linked firmly together.
Because of their small size, monomers can enter cells and cause harm. Polymers are typically large enough that they do not enter cells. However, their manufacture and disposal causes adverse impacts.
Halogenated (or organohalogen) flame retardants
- These flame retardants are among the most widely used and most problematic. Many organohalogen flame retardants have been banned or phased out, but others have not been adequately tested and are likely to cause similar harm.
Organophosphate flame retardants
- These flame retardants, similar in structure and action to organophosphate pesticides, are replacing organohalogens. Research suggests they are not a better choice. Some have been associated with harm to the nervous, reproductive, and skeletal systems.
Polymeric flame retardants
- These large molecules are often marketed as safer because their size makes it difficult for them to enter cells. However, their manufacture and disposal can cause contamination.
Are PFAS flame retardants?
- PFAS chemicals are used in firefighting foam to extinguish actively burning petroleum-based fires. With a few exceptions, they are different from flame retardants, which are intended to delay fire ignition. Learn more about PFAS.
Learn about specific flame retardant chemicals here.
What is being done?
The Green Science Policy Institute works with manufacturers, retailers, large purchasers, regulators, and NGOs to limit the use of flame retardants for safer furniture, electronics, and building insulation.

We helped draft the San Antonio Statement on Brominated and Chlorinated Flame Retardants. This scientific consensus statement on the health harm and lack of fire safety benefit of organohalogens has over 200 signatories from 30 countries.
Local, national, and international regulations have limited the use of some harmful flame retardants. The Stockholm Convention is a treaty between over 150 countries, not including the U.S., which aims to reduce the release of persistent organic pollutants. Several organohalogen flame retardants are banned by the convention.
What can you do?
Learn how to limit your exposure to toxic chemicals and safer products on our consumer resources page.
- When buying upholstered furniture, look for a TB 117-2013 label stating the item does not contain flame retardants.
- Replace upholstered furniture with a TB 117 label.
- Furniture and children’s products filled with polyester or wool instead of foam are unlikely to contain added flame retardants.
- To reduce indoor dust levels, vacuum with a HEPA filter, wet mop, and dust with a damp cloth.
- Wash hands often, especially before eating or preparing food.
- Avoid using rebonded carpet padding made from recycled or scrap polyurethane foam.
- Tell manufacturers, retailers, and government agencies you want products without flame retardants.
Video
Flame Retardants: Four-minute introduction
Decision: U.S. CPSC votes to ban organohalogen flame retardants in some products
Where have all the toxic chemicals gone? Arlene Blum at TEDx Wellesley College
Toxic Chemical Soup: Arlene Blum on flame retardants